987.Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree¶
Tags: Hash Table Tree Medium
Links: https://leetcode.com/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree/
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
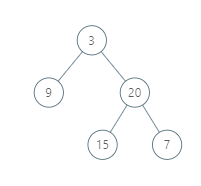
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
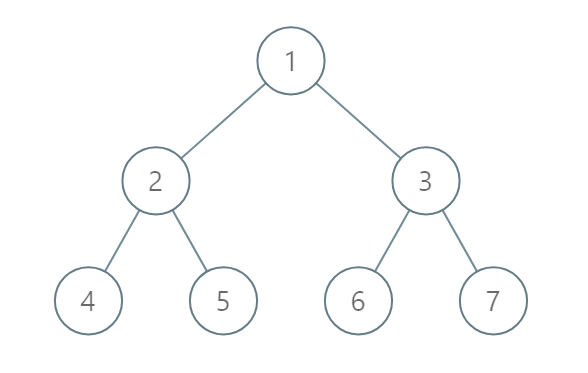
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
第一种解法:
map里面嵌套map:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
map<int, map<int, vector<int>>> mp;
void traverse(TreeNode* root, int pos, int level)
{
mp[pos][level].push_back(root -> val);
if (root -> left) traverse(root -> left, pos - 1, level + 1);
if (root -> right) traverse(root -> right, pos + 1, level + 1);
}
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root) return res;
traverse(root, 0, 0);
for(auto it : mp)
{
vector<int> cur;
for(auto it2 : it.second)
{
vector<int> &tmp = it2.second;
sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
for(int i = 0; i < tmp.size(); ++i)
cur.push_back(tmp[i]);
}
res.push_back(cur);
}
return res;
}
};
Runtime: 12 ms, faster than 17.63% of C++ online submissions for Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree.
Memory Usage: 16.3 MB, less than 22.22% of C++ online submissions for Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary
思路是利用节点的位置pos作为键,由层数和节点组成的map作为值,所以遍历存在两层循环,第一层是把所有处于同一列的节点放置于同一数组内,第二层是对同一个数组内的元素根据层数由上层到下层来排序。
第二种方法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
map<pair<int, int>, vector<int>> mp;
void traverse(TreeNode* root, int pos, int level)
{
mp[make_pair(pos, level)].push_back(root -> val);
if (root -> left) traverse(root -> left, pos - 1, level + 1);
if (root -> right) traverse(root -> right, pos + 1, level + 1);
}
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root) return res;
traverse(root, 0, 0);
int lastPos = INT_MIN;
for(auto pr : mp)
{
int pos = pr.first.first; //节点所在的列
vector<int> tmp(pr.second);
sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
if (pos != lastPos) {
res.push_back(tmp);
}
else {
for (auto e : tmp) res[res.size() - 1].push_back(e);
}
lastPos = pos;
}
return res;
}
};
这种方法是把坐标pos, level作为键,每个坐标对应的节点作为值,因为map已经对坐标进行了排序,所以考虑的是当pos也就是列相同但层数不同的情况。所以用一个变量lastPos来记录上一次循环的pos值,如果相同,那么说明当前的vector和上一次的属于同一列,那么就把当前数组的元素加入到最终数组最后一个数组里面。如果pos != lastPos,说明它们属于不同的列,所以最终数组新增一个数组(注意,前面的情况没有新增数组).