160.Intersection of Two Linked Lists¶
Tags: Easy Linked List
Links: https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
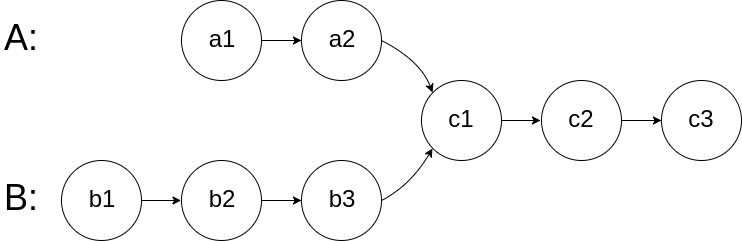
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
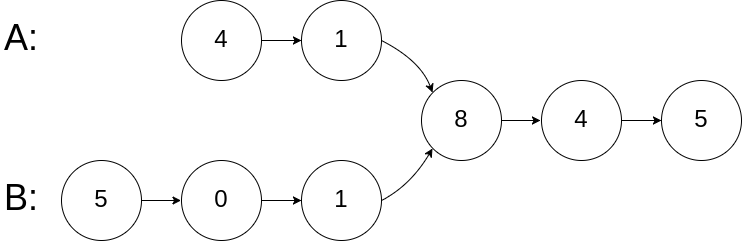
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
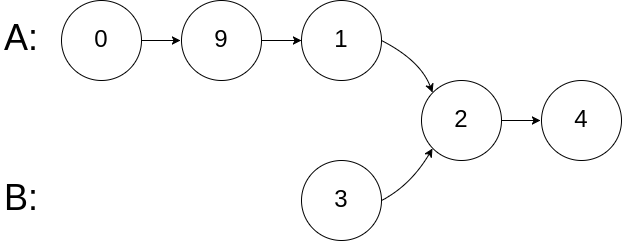
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
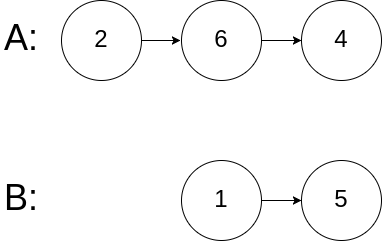
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: null
Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null. - The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
if (!headA || !headB) return nullptr;
ListNode *l1 = headA, *l2 = headB;
while (headA -> next) headA = headA -> next;
while (headB -> next) headB = headB -> next;
if (headA != headB) return nullptr;
headA -> next = l1;
ListNode *slow = l2 -> next, *fast = l2 -> next -> next;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow -> next;
fast = fast -> next -> next;
}
fast = l2;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow -> next;
fast = fast -> next;
}
headA -> next = nullptr;
return fast;
}
};
思路是先判断两个链表是否存在交点,如果存在交点,就把其中一条链首尾相连,然后就变成了寻找链表中环的入口的方法。