1515.Best Position for a Service Centre¶
Tags: Hard Geometry
Links: https://leetcode.com/problems/best-position-for-a-service-centre/
A delivery company wants to build a new service centre in a new city. The company knows the positions of all the customers in this city on a 2D-Map and wants to build the new centre in a position such that the sum of the euclidean distances to all customers is minimum.
Given an array positions where positions[i] = [xi, yi] is the position of the ith customer on the map, return the minimum sum of the euclidean distances to all customers.
In other words, you need to choose the position of the service centre [xcentre, ycentre] such that the following formula is minimized:
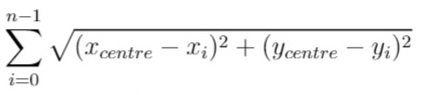
Answers within 10^-5 of the actual value will be accepted.
Example 1:
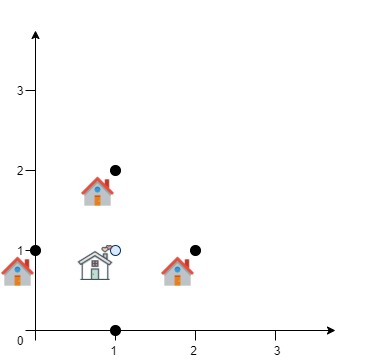
Input: positions = [[0,1],[1,0],[1,2],[2,1]]
Output: 4.00000
Explanation: As shown, you can see that choosing [xcentre, ycentre] = [1, 1] will make the distance to each customer = 1, the sum of all distances is 4 which is the minimum possible we can achieve.
Example 2:
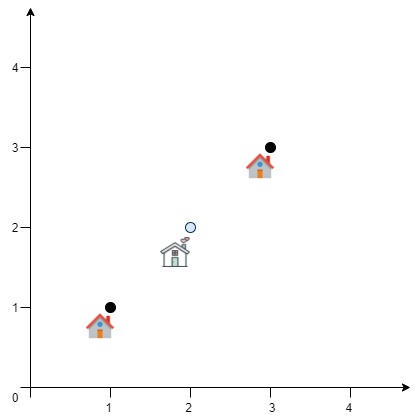
Input: positions = [[1,1],[3,3]]
Output: 2.82843
Explanation: The minimum possible sum of distances = sqrt(2) + sqrt(2) = 2.82843
Example 3:
Input: positions = [[1,1]]
Output: 0.00000
Example 4:
Input: positions = [[1,1],[0,0],[2,0]]
Output: 2.73205
Explanation: At the first glance, you may think that locating the centre at [1, 0] will achieve the minimum sum, but locating it at [1, 0] will make the sum of distances = 3.
Try to locate the centre at [1.0, 0.5773502711] you will see that the sum of distances is 2.73205.
Be careful with the precision!
Example 5:
Input: positions = [[0,1],[3,2],[4,5],[7,6],[8,9],[11,1],[2,12]]
Output: 32.94036
Explanation: You can use [4.3460852395, 4.9813795505] as the position of the centre.
Constraints:
1 <= positions.length <= 50positions[i].length == 20 <= positions[i][0], positions[i][1] <= 100\
Weber问题:求平面上的供给点到需求点的最小欧几里得距离和。
Weiszfeld算法:通过以下迭代式进行迭代更新,自定义求解精度。其中x, y代表上一轮的供给点的横纵坐标,x', y'代表新一轮的供给点横纵坐标。
初始化时,我们用横纵坐标的平均值作为初始点,然后不断迭代更新。注意可能存在分母为0的情况。
class Solution {
public:
double getMinDistSum(vector<vector<int>>& positions) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n = positions.size();
double eps = 1e-8;
double x, y;
double sum_x = 0, sum_y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
sum_x += positions[i][0];
sum_y += positions[i][1];
}
x = sum_x / n, y = sum_y / n;
double pre_x = x, pre_y = y;
while (true) {
double sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0, sum3 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
double tmp = dis(x, y, positions[i][0], positions[i][1]);
if (tmp < eps) continue;
sum1 += (double)positions[i][0] / tmp;
sum2 += (double)positions[i][1] / tmp;
sum3 += (double)1 / tmp;
}
if (sum3 < eps) break;
pre_x = x, pre_y = y;
x = sum1 / sum3, y = sum2 / sum3;
if (abs(x - pre_x) < eps && abs(y - pre_y) < eps) break;
}
double res = 0;
for (auto & e : positions) res += dis(x, y, e[0], e[1]);
return res;
}
inline double dis(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
return sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
}
};
模拟退火:
class Solution {
public:
double getMinDistSum(vector<vector<int>>& positions) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n = positions.size();
double resX = 0, resY = 0;
for (auto & e : positions) {
resX += e[0], resY += e[1];
}
resX /= n, resY /= n;
double resW = energy(resX, resY, positions);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
SA(resX, resY, resW, positions);
}
return resW;
}
double energy(double x, double y, vector<vector<int>>& positions)
{
double res = 0;
for (auto & e : positions) {
double tmpX = x - e[0];
double tmpY = y - e[1];
res += sqrt(tmpX * tmpX + tmpY * tmpY);
}
return res;
}
void SA(double & resX, double & resY, double & resW, vector<vector<int>>& positions)
{
double T = 3000;
const double EPS = 1e-15;
while (T > EPS) {
double nextX = resX + ((long long)rand() * 2 - RAND_MAX) * T;
double nextY = resY + ((long long)rand() * 2 - RAND_MAX) * T;
double nextW = energy(nextX, nextY, positions);
double delta = nextW - resW;
if (delta < 0) {
resX = nextX, resY = nextY, resW = nextW;
}
else if (exp(- delta / T) * RAND_MAX > rand()) {
resX = nextX, resY = nextY;
}
T *= 0.995;
}
}
};