1496.Path Crossing¶
Tags: String Hash Table Easy
Links: https://leetcode.com/problems/path-crossing/
Given a string path, where path[i] = 'N', 'S', 'E' or 'W', each representing moving one unit north, south, east, or west, respectively. You start at the origin (0, 0) on a 2D plane and walk on the path specified by path.
Return True if the path crosses itself at any point, that is, if at any time you are on a location you've previously visited. Return False otherwise.
Example 1:
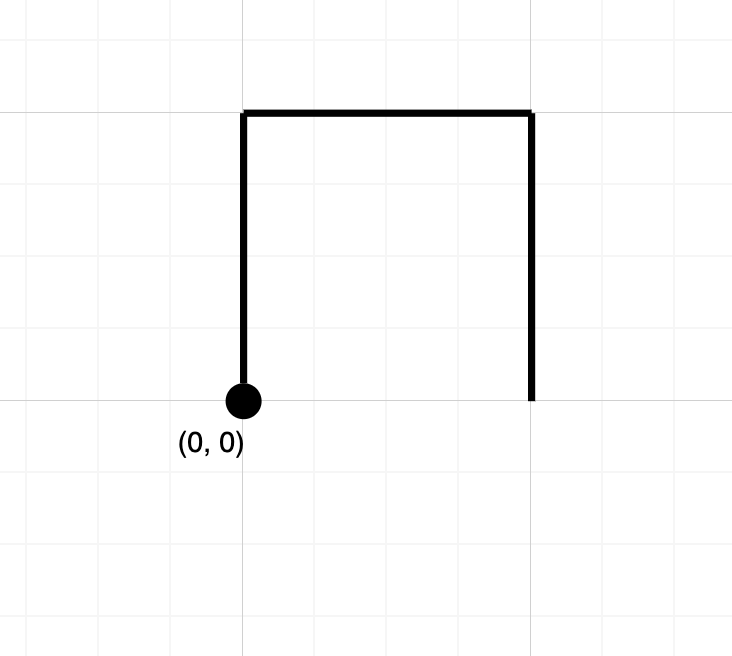
Input: path = "NES"
Output: false
Explanation: Notice that the path doesn't cross any point more than once.
Example 2:
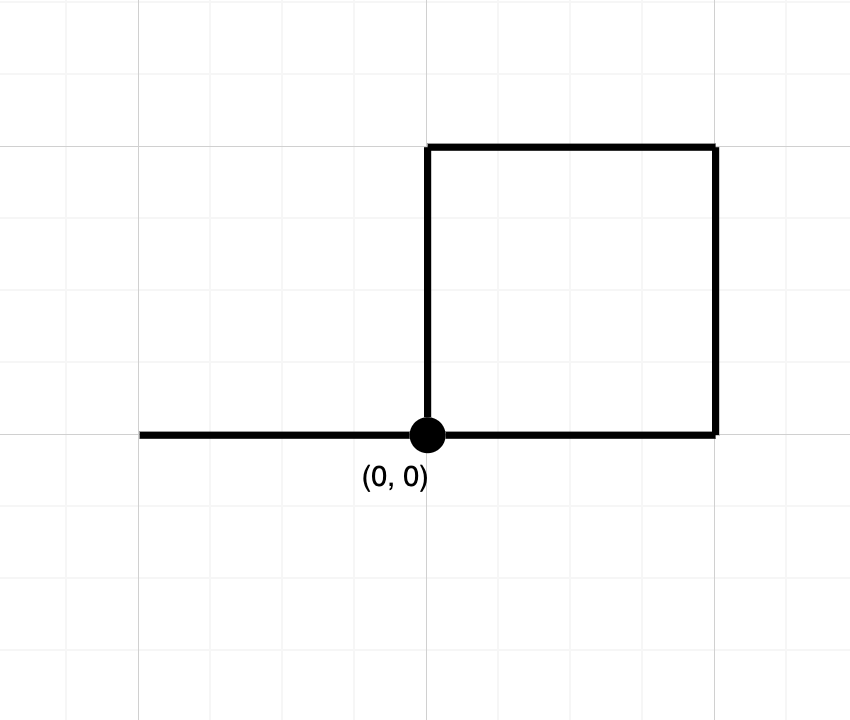
Input: path = "NESWW"
Output: true
Explanation: Notice that the path visits the origin twice.
Constraints:
1 <= path.length <= 10^4pathwill only consist of characters in{'N', 'S', 'E', 'W}
一种很直接的想法就是建立一个哈希表存储横纵坐标,每次判断当前位置是否已经被访问过了,这样就需要存储横纵坐标两个数据,比较占据存储空间。优化的办法就是只存储一个数据,但是这个数据要能反应横纵坐标的信息,所以想到把横纵坐标看成字符串,采用字符串哈希(自然溢出)的办法。
class Solution {
typedef unsigned long long ull;
static constexpr ull Base = 13331;
unordered_set<ull> us;
public:
bool isPathCrossing(string path) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int x = 0, y = 0;
insert(x, y);
for (auto & e : path) {
if (e == 'N') { if (!insert(x, ++y)) return true; }
else if (e == 'S') { if (!insert(x, --y)) return true; }
else if (e == 'E') { if (!insert(++x, y)) return true; }
else { if (!insert(--x, y)) return true; }
}
return false;
}
bool insert(int x, int y)
{
string s = to_string(x) + to_string(y);
ull tmp = 0;
for (auto & e : s) tmp = tmp * Base + e;
if (us.find(tmp) != us.end()) return false;
us.emplace(tmp);
return true;
}
};