1484.Clone Binary Tree With Random Pointer¶
Tags: Medium Tree
Links: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/clone-binary-tree-with-random-pointer/
A binary tree is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the tree or null.
Return a deep copy of the tree.
The tree is represented in the same input/output way as normal binary trees where each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (in the input) where the random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
You will be given the tree in class Node and you should return the cloned tree in class NodeCopy.
Example 1:
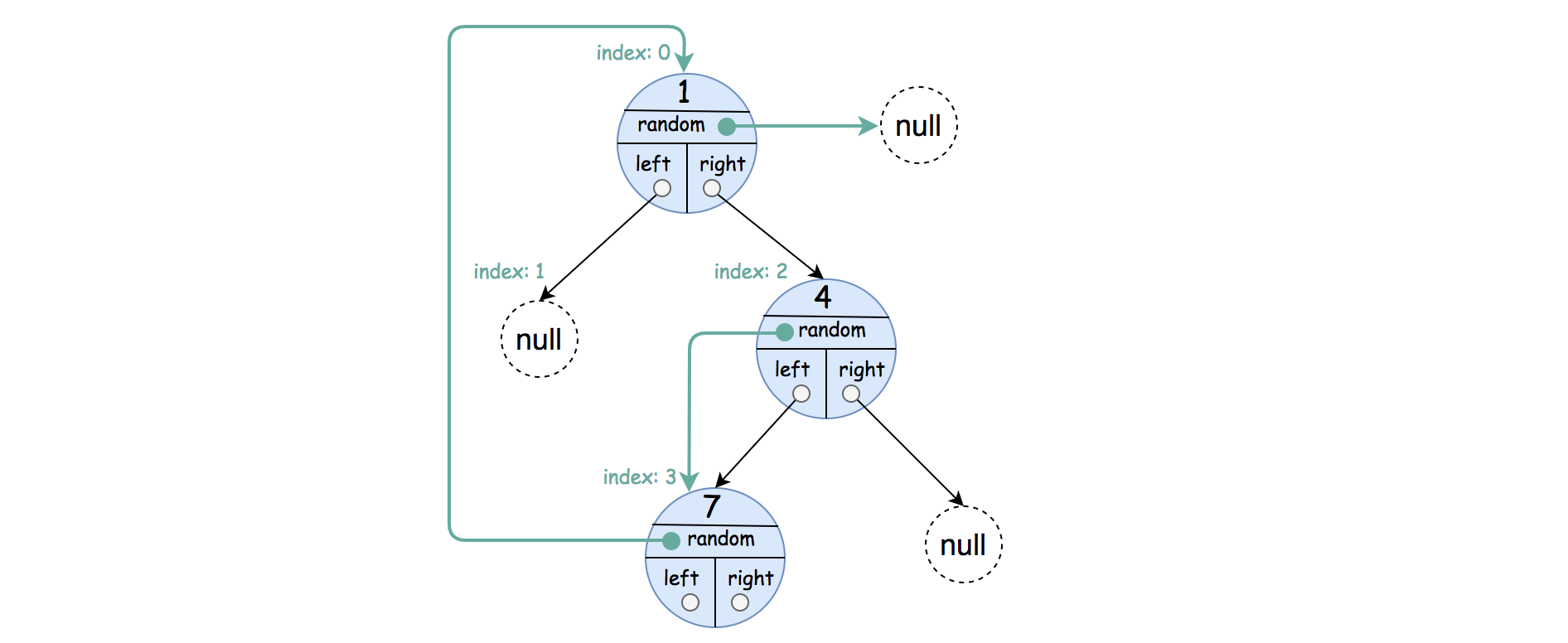
Input: root = [[1,null],null,[4,3],[7,0]]
Output: [[1,null],null,[4,3],[7,0]]
Explanation: The original binary tree is [1,null,4,7].
The random pointer of node one is null, so it is represented as [1, null].
The random pointer of node 4 is node 7, so it is represented as [4, 3] where 3 is the index of node 7 in the tree array.
The random pointer of node 7 is node 1, so it is represented as [7, 0] where 0 is the index of node 1 in the tree array
Example 2:
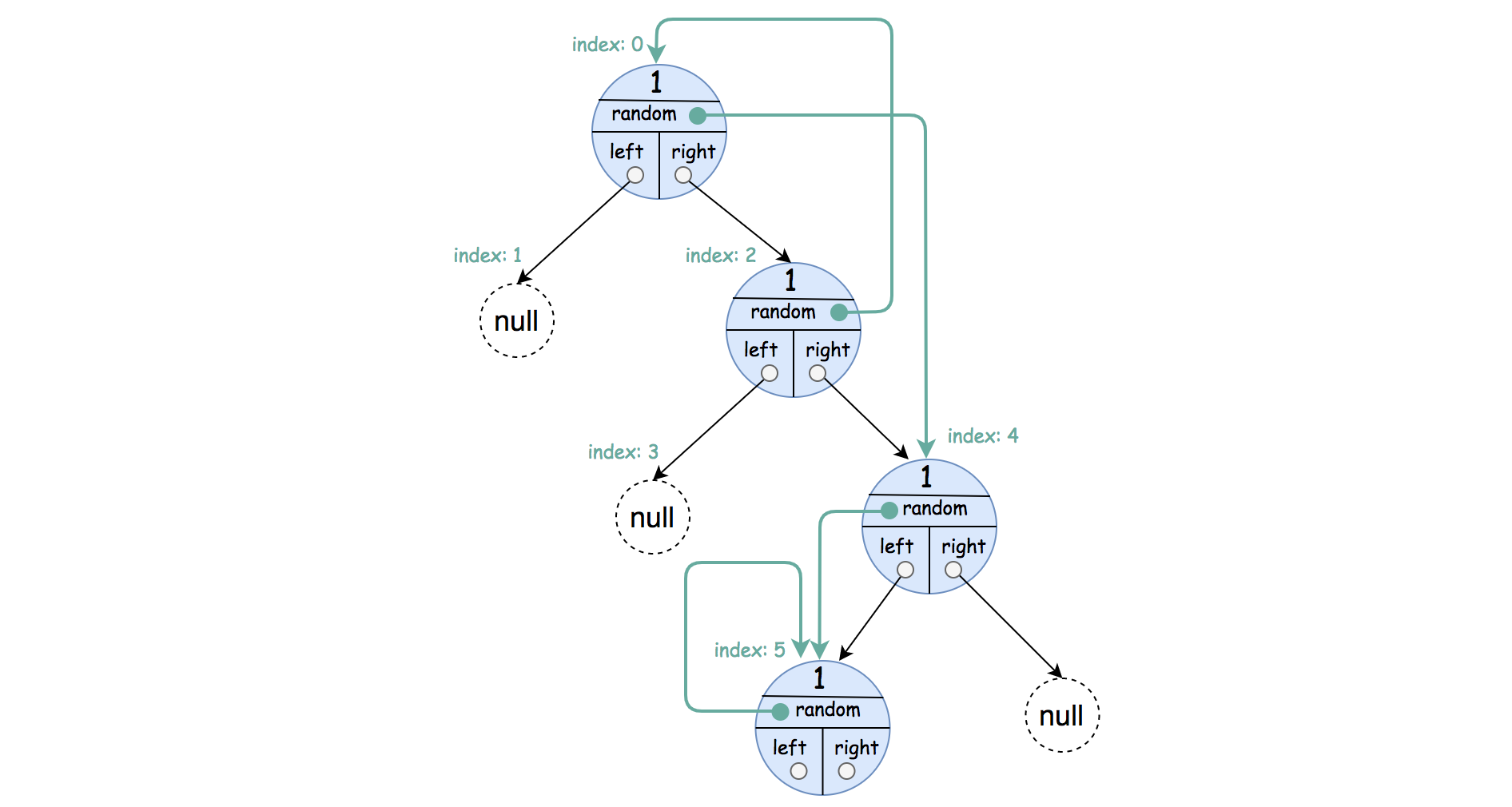
Input: root = [[1,4],null,[1,0],null,[1,5],[1,5]]
Output: [[1,4],null,[1,0],null,[1,5],[1,5]]
Explanation: The random pointer of a node can be the node itself.
Example 3:
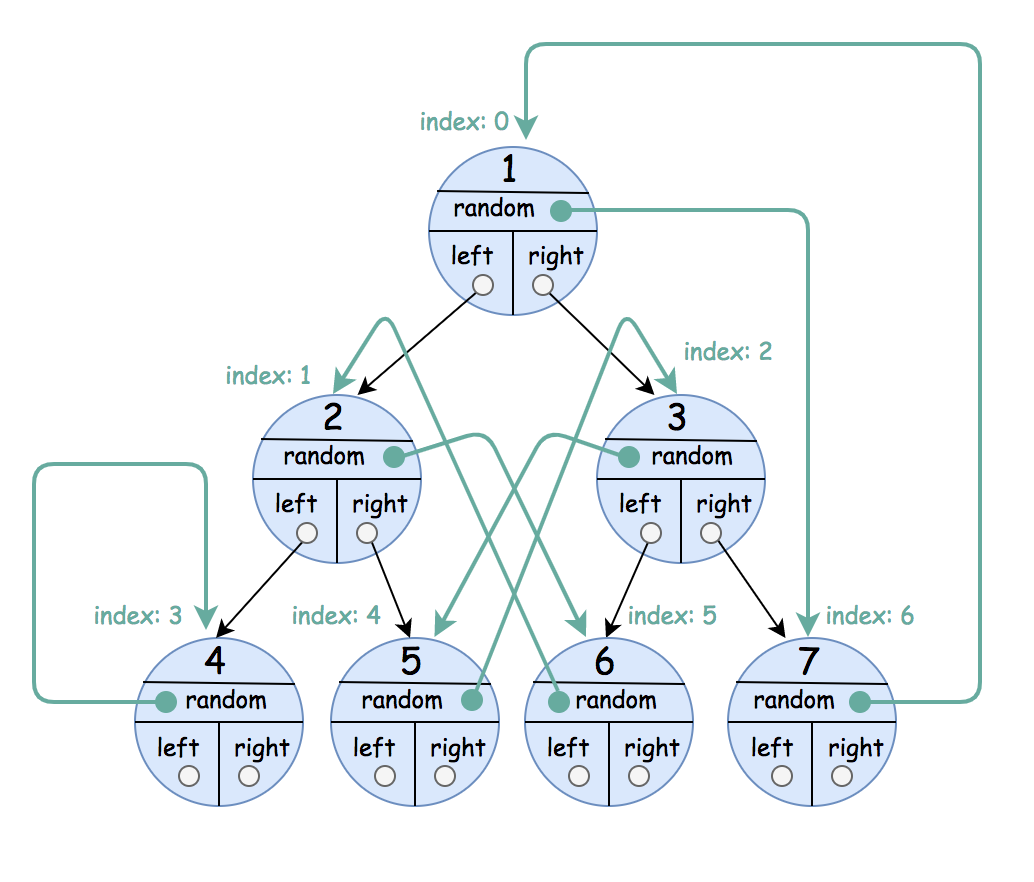
Input: root = [[1,6],[2,5],[3,4],[4,3],[5,2],[6,1],[7,0]]
Output: [[1,6],[2,5],[3,4],[4,3],[5,2],[6,1],[7,0]]
Example 4:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 5:
Input: root = [[1,null],null,[2,null],null,[1,null]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 1000]. - Each node's value is between
[1, 10^6].
看到深拷贝第一个想到的就是LeetCode 138的对带随机指针的链表的深拷贝,两个题目其实是一样的,都可以用哈希表来加速,也就是建立一个unordered_map,键是Node *,值是NodeCopy *,也就是建立原二叉树的每个节点和深拷贝后的二叉树的节点的对应。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* Node *left;
* Node *right;
* Node *random;
* Node() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr), random(nullptr) {}
* Node(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr), random(nullptr) {}
* Node(int x, Node *left, Node *right, Node *random) : val(x), left(left), right(right), random(random) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
unordered_map<Node *, NodeCopy *> um;
public:
NodeCopy* copyRandomBinaryTree(Node* root) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
if (!root) return NULL;
if (um.find(root) == um.end()) {
um[root] = new NodeCopy(root -> val);
um[root] -> left = copyRandomBinaryTree(root -> left);
um[root] -> right = copyRandomBinaryTree(root -> right);
um[root] -> random = copyRandomBinaryTree(root -> random);
}
return um[root];
}
};