1457.Pseudo-Palindromic Paths in a Binary Tree¶
Tags: Medium Depth-first Search Bit Manipulation Tree
Links: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pseudo-palindromic-paths-in-a-binary-tree/
Given a binary tree where node values are digits from 1 to 9. A path in the binary tree is said to be pseudo-palindromic if at least one permutation of the node values in the path is a palindrome.
Return the number of **pseudo-palindromic* paths going from the root node to leaf nodes.*
Example 1:
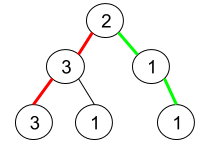
Input: root = [2,3,1,3,1,null,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the red path [2,3,3], the green path [2,1,1], and the path [2,3,1]. Among these paths only red path and green path are pseudo-palindromic paths since the red path [2,3,3] can be rearranged in [3,2,3] (palindrome) and the green path [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 2:
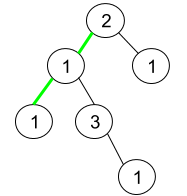
Input: root = [2,1,1,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,1]
Output: 1
Explanation: The figure above represents the given binary tree. There are three paths going from the root node to leaf nodes: the green path [2,1,1], the path [2,1,3,1], and the path [2,1]. Among these paths only the green path is pseudo-palindromic since [2,1,1] can be rearranged in [1,2,1] (palindrome).
Example 3:
Input: root = [9]
Output: 1
Constraints:
- The given binary tree will have between
1and10^5nodes. - Node values are digits from
1to9.
题意是遍历所有从根节点到叶节点的路径,这些路径有多少可以组成回文。
于是问题的两个核心矛盾:
- 如何遍历二叉树的所有路径?方法的原型就是LintCode 480. 二叉树的所有路径,或者LeetCode 112.Path Sum,会有一定程度的接近。考察的是DFS,所以要记得恢复状态。
- 如何判断路径上的数字能否组成回文?因为限定了数值都是1 - 9之间,可以用一个长度为10的数组去统计路径上数字出现的频率。能构成回文的条件是最多有一个数字出现奇数次。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
vector<int> num;
int res;
public:
int pseudoPalindromicPaths (TreeNode* root) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
if (!root) return 0;
num.resize(10, 0);
res = 0;
traversal(root);
return res;
}
void traversal(TreeNode *root)
{
++num[root -> val];
if (root -> left) {
traversal(root -> left);
--num[root -> left -> val];
}
if (root -> right) {
traversal(root -> right);
--num[root -> right -> val];
}
if (!root -> left && !root -> right) {
if (check()) ++res;
}
}
inline bool check()
{
int odd = 0, even = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
if (num[i] & 1) ++odd;
else ++even;
}
return odd <= 1;
}
};