1206.Design Skiplist¶
Tags: Hard Design
Links: https://leetcode.com/problems/design-skiplist/
Design a Skiplist without using any built-in libraries.
A Skiplist is a data structure that takes O(log(n)) time to add, erase and search. Comparing with treap and red-black tree which has the same function and performance, the code length of Skiplist can be comparatively short and the idea behind Skiplists are just simple linked lists.
For example: we have a Skiplist containing [30,40,50,60,70,90] and we want to add 80 and 45 into it. The Skiplist works this way:
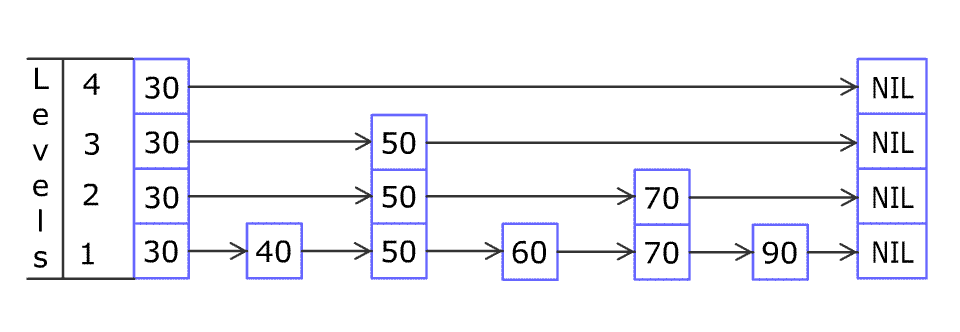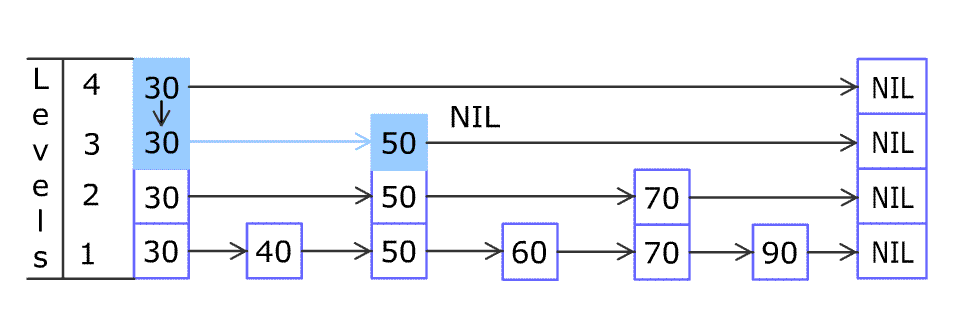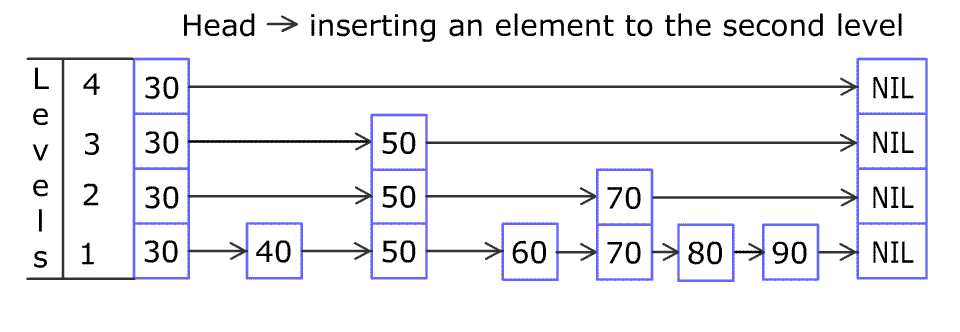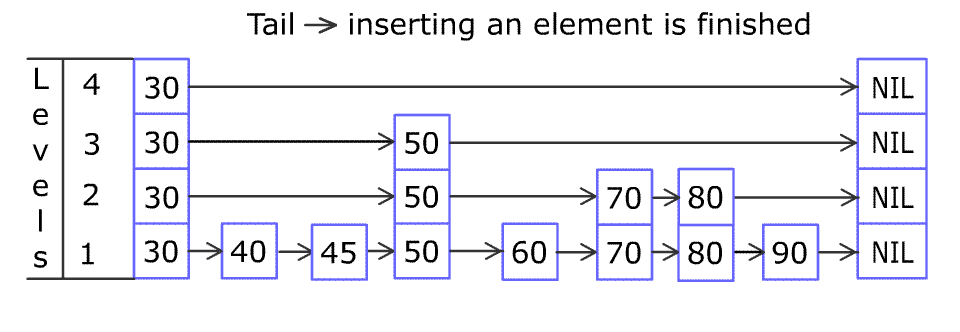 Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
You can see there are many layers in the Skiplist. Each layer is a sorted linked list. With the help of the top layers, add , erase and searchcan be faster than O(n). It can be proven that the average time complexity for each operation is O(log(n)) and space complexity is O(n).
To be specific, your design should include these functions:
bool search(int target): Return whether thetargetexists in the Skiplist or not.void add(int num): Insert a value into the SkipList.bool erase(int num): Remove a value in the Skiplist. Ifnumdoes not exist in the Skiplist, do nothing and return false. If there exists multiplenumvalues, removing any one of them is fine.
See more about Skiplist : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
Note that duplicates may exist in the Skiplist, your code needs to handle this situation.
Example:
Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist();
skiplist.add(1);
skiplist.add(2);
skiplist.add(3);
skiplist.search(0); // return false.
skiplist.add(4);
skiplist.search(1); // return true.
skiplist.erase(0); // return false, 0 is not in skiplist.
skiplist.erase(1); // return true.
skiplist.search(1); // return false, 1 has already been erased.
Constraints:
0 <= num, target <= 20000- At most
50000calls will be made tosearch,add, anderase.
跳表的三个操作,查找、插入和删除。每个操作的时间复杂度均为\log n。
struct Node
{
Node *right, *down;
int val;
Node(Node *right, Node *down, int val) : right(right), down(down), val(val) {}
};
class Skiplist {
Node *head;
public:
Skiplist() {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
head = new Node(NULL, NULL, INT_MIN);
}
bool search(int target) {
Node *p = head;
while (p) {
while (p -> right && p -> right -> val < target) p = p -> right;
//查找到末尾或者下一个数大于tartget
//表明本层不存在目标值
if (!p -> right || p -> right -> val > target) p = p -> down;
else return true; //查找到了目标值
}
return false;
}
void add(int num) {
Node *p = head;
vector<Node *> path; //记录自顶向下的路径
while (p) {
while (p -> right && p -> right -> val < num) p = p -> right;
path.push_back(p);
p = p -> down;
}
bool insertUp = true; //是否继续在上一层插入节点
Node *downNode = NULL; //指向当前层的下一层节点
while (insertUp && path.size()) {
Node *tmp = path.back(); path.pop_back();
tmp -> right = new Node(tmp -> right, downNode, num); //插入一个新的节点
downNode = tmp -> right; //downNode指向新的节点
insertUp = rand() & 1; //50%的概率在上一层插入节点
}
if (insertUp) { //如果需要新开一层
Node *nextNode = new Node(NULL, downNode, num);
head = new Node(nextNode, head, INT_MIN);
}
}
bool erase(int num) {
Node *p = head;
bool canDelete = false;
while (p) {
while (p -> right && p -> right -> val < num) p = p -> right;
if (!p -> right || p -> right -> val > num) p = p -> down;
else { //找到需要删除的节点,只需删除一个
canDelete = true;
Node *tmp = p -> right;
p -> right = tmp -> right;
delete tmp; tmp = NULL;
p = p -> down;
}
}
return canDelete;
}
};
/**
* Your Skiplist object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Skiplist* obj = new Skiplist();
* bool param_1 = obj->search(target);
* obj->add(num);
* bool param_3 = obj->erase(num);
*/